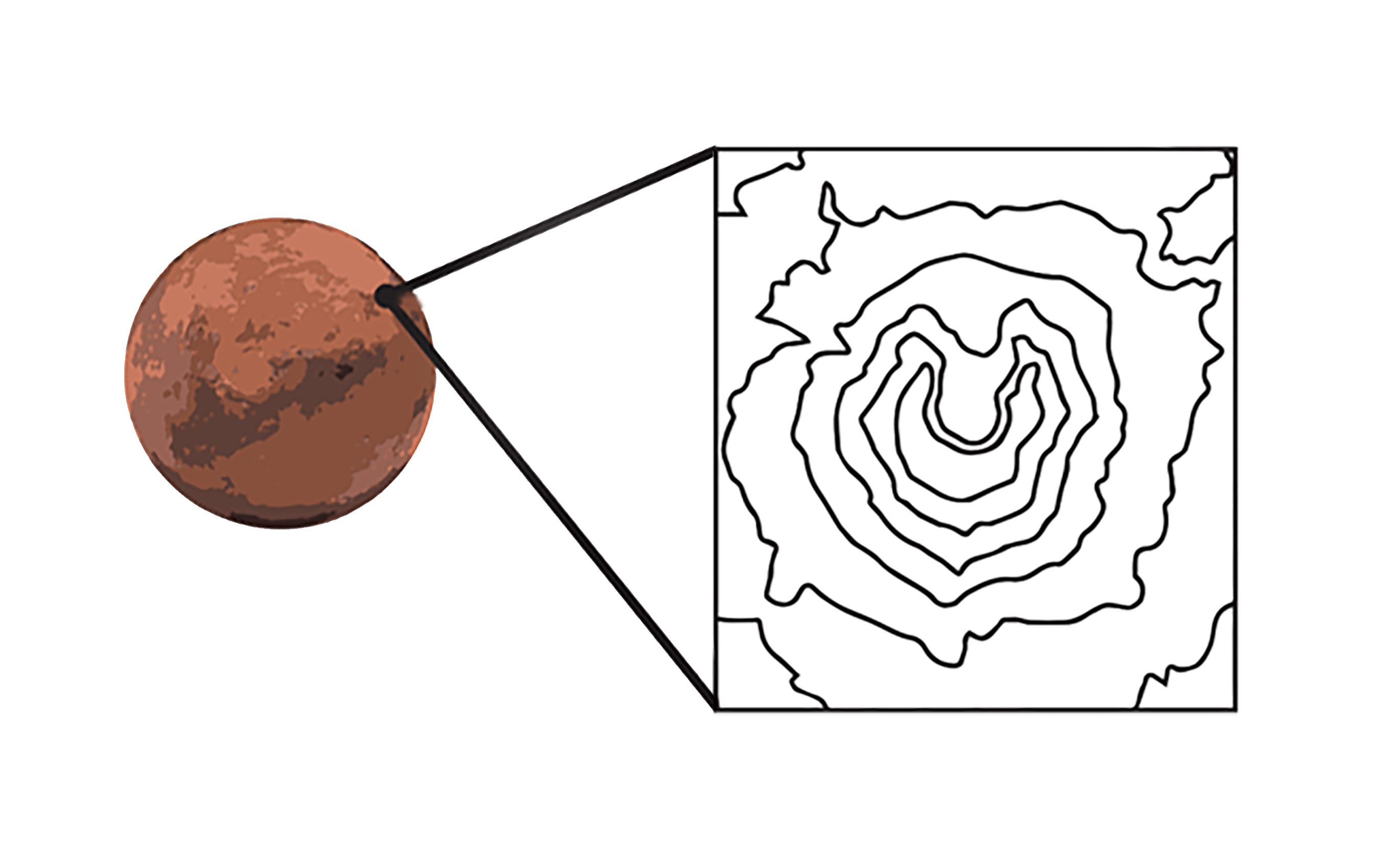
Design technologies to learn about the surface of a mystery moon and use NASA Mars data to choose a landing site for a rover!

How to Teach These Units
What is Engineering?
Youth engineer a tower to support a model antenna and reflect on the Engineering Design Process they used.
Youth Will Know
- Engineers use an Engineering Design Process as a tool to solve problems.
- Technology is any object, system, or process designed by people to solve a problem.
Activity Downloads
|
P1_What_Is_Engineering_Educator_Guide
What is Engineering Activity Guide
|
|
|
P1_What_Is_Engineering_Engineering_Journal
What is Engineering Notebook (English)
|
|
|
P1_What_Is_Engineering_Engineering_Journal_Spanish
What is Engineering Notebook (Spanish)
|
Setup
The Educator Guide has a script, materials list, and prep directions. Be sure to have it open and ready to help guide you through every activity. It will take about 5 minutes to prepare for this activity.
- Prepare a model antenna. Fold one index card in half widthwise and clip three binder clips to it.
- Arrange 100 index cards, a ruler, and a pair of scissors for each group on the Materials Table.
- Place 4 rolls of masking tape on the Materials Table for groups to share.
Guiding Question
How can we design something to solve a problem?
Youth Will Do
- Use the Engineering Design Process.
- Work together to engineer a tower to support a model antenna.
Did You Know?
- Use duct tape much? You probably engineer more than you think. Anytime you design a makeshift tool because you don't have exactly what you need, you are engineering.
Quick Tips
- Help youth see that they naturally did each of steps of the EDP as they engaged in the design challenge.
- If youth want to fix their designs, highlight the 'Improve' step on the EDP. If you don't have extra time, tell youth they will have a whole period to improve future designs in Activity 5.
Glossary
- Criteria: things that you or your design needs to do
- Constraints: ways that you or your design are limited
Activity Timing
Engineering Showcase
Youth communicate their knowledge of remote sensing devices and the information they gathered about the Mystery Moon at the Engineering Showcase.
Youth Will Know
- Communicating with others is an important part of the Engineering Design Process.
- As engineers, they have valuable knowledge to share about the problem they have solved.
- They can communicate their recommendations based on the data they collected with their remote sensing technologies.
Activity Downloads
|
A6_Engineering_Showcase_Educator_Guide
Engineering Showcase Educator Guide
|
|
|
A6_Engineering_Showcase_Engineering_Notebook
Engineering Showcase Engineering Notebook (English)
|
|
|
A6_Engineering_Showcase_Engineering_Notebook_Spanish
Engineering Showcase Engineering Notebook (Spanish)
|
Setup
The Educator Guide has a script, materials list, and prep directions. Be sure to have it open and ready to help guide you through every activity.
- Post the Engineering Design Process poster.
- Arrange the Space Screens as in Activities 4 and 5.
- Create a Materials Table with the materials from Activity 4.
- Invite people from the community (including families and friends of youth) to the Engineering Showcase, and assign roles using the Scientist Cards.
Guiding Question
How can we share information about our remote sensing technology design with others?
Youth Will Do
- Prepare a final presentation.
- Recommend a site using the data they have gathered as evidence.
Did You Know?
- Engineers and scientists present their discoveries and inventions all the time at professional conferences around the world. In academia, this is called scholarship.
Quick Tips
- If you do not have an opportunity to brief the visitors playing the scientists, have one or more youth provide a summary of the different missions.
- Ask questions to help youth accurately communicate their results.
Glossary
Communicate (in engineering): to share information, data, or ideas in order to improve designs or inspire new designs
Activity Timing
Improve
Youth improve their device, decide how to display the data, and make a recommendation to the scientist.
Youth Will Know
- The improve step allows engineers to reflect upon and alter their designs.
- They can improve remote sensing technologies.
Activity Downloads
|
A5_Improve_Educator_Guide
Improve Educator Guide
|
|
|
A5_Improve_Engineering_Notebook
Improve Engineering Notebook (English)
|
|
|
A5_Improve_Engineering_Notebook_Spanish
Improve Engineering Notebook (Spanish)
|
Setup
The Educator Guide has a script, materials list, and prep directions. Be sure to have it open and ready to help guide you through every activity.
- Post the Engineering Design Process poster.
- Arrange the Space Screens according to Space Screen Assembly, Educator Guide p. 52.
- Create a Materials Table with the materials from Activity 4.
- Make copies of the Engineering Showcase invitation, Educator Guide p. 83, for youth to distribute to their family and friends.
Guiding Question
How can we improve our remote sensing devices?
Youth Will Do
- Improve their remote sensing devices.
- Start to think about how they will communicate the data they collected to the scientists.
Did You Know?
- Data can be communicated in music or visually appealing artforms. Try it yourself: assign a note to each level of the moonscape and sing or play your findings to the group.
Quick Tips
- Have groups check the size of their devices by placing them on a folded sheet of paper.
- Data visualizations can take many forms, including drawings, maps, and graphs.
- Having an authentic audience for the Showcase can inspire youth to think more deeply about their presentations.
Glossary
Improve (in engineering): To make a device better than the first build. Examples include something being smaller, lighter, more durable, faster, able to do more things, or collect more kinds of data.
Activity Timing
Create a Remote Sensing Device
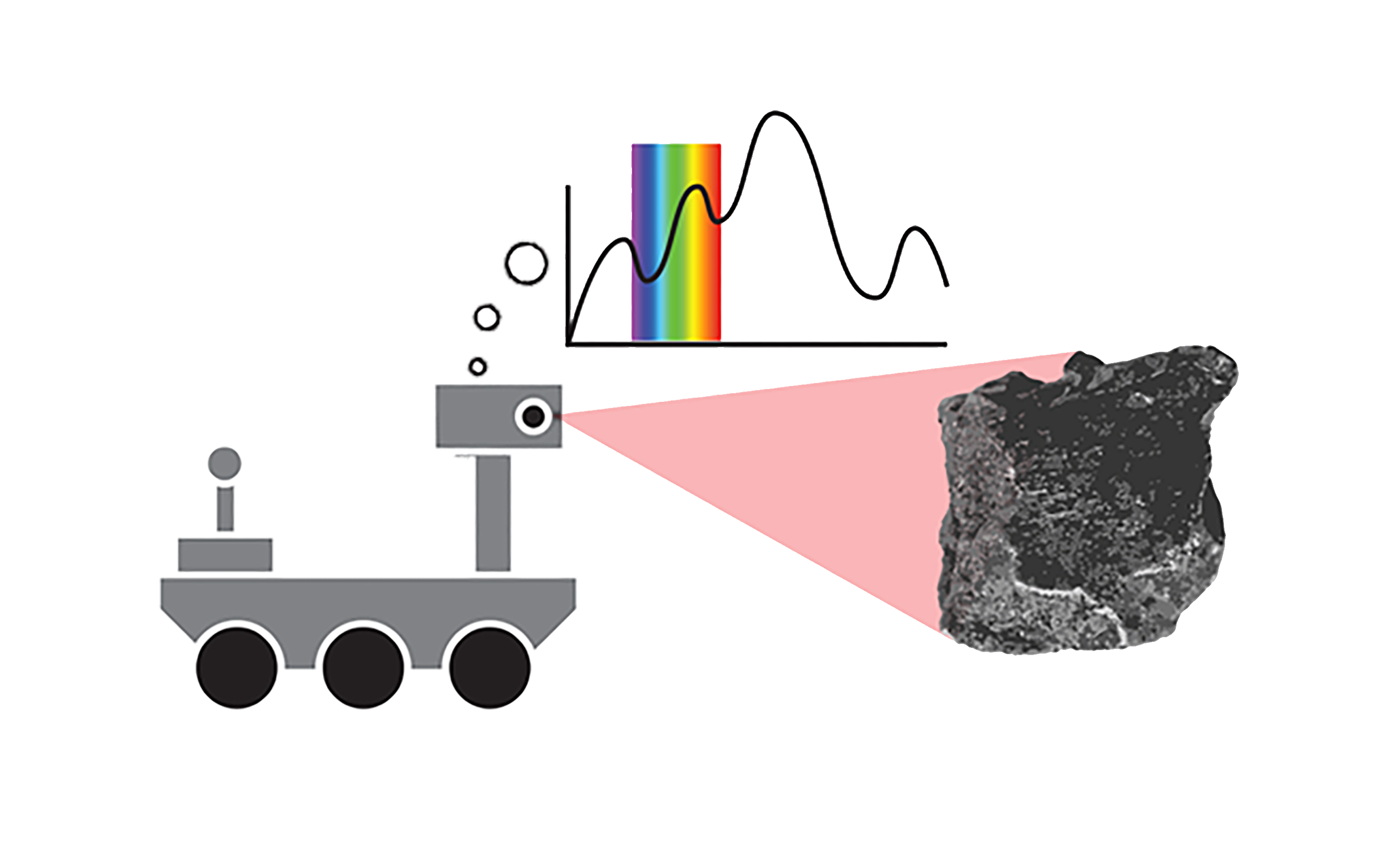
Youth apply what they have learned so far to design remote sensing devices to answer a question posed by a scientist.
Youth Will Know
- As engineers, they can design remote sensing technologies to get information about a Mystery Moon from a distance.
- Using the steps of the Engineering Design Process can help guide them to a successful solution.
- Engineers use what they learn in the identify and investigate step to inform their design decisions.
- Engineers often collaborate with scientists to determine the criteria and constraints of a project.
Activity Downloads
|
A4_Create_a_Remote_Sensing_Device_Educator_Guide
Create a Remote Sensing Device Educator Guide
|
|
|
A4_Create_a_Remote_Sensing_Device_Engineering_Notebook
Create a Remote Sensing Device Engineering Notebook (English)
|
|
|
A4_Create_a_Remote_Sensing_Device_Engineering_Notebook_Spanish
Create a Remote Sensing Device Engineering Notebook (Spanish)
|
Setup
The Educator Guide has a script, materials list, and prep directions. Be sure to have it open and ready to help guide you through every activity.
- Post the Engineering Design Process poster.
- Prepare the Mystery Moon sites and Space Screens by following the instructions on Educator Guide pp. 51–53.
- Create a Materials Table with the materials listed in the guide.
Guiding Question
How can we create remote sensing technologies to gather different types of data from a distance?
Youth Will Do
- Work in groups to plan, create, and test remote sensing devices that can collect information about the Mystery Moon.
Did You Know?
- Failure is a big part of the Engineering Design Process. Engineers sometimes make mistakes on purpose so they can learn how to avoid them later when it's more crucial to get it right.
Quick Tips
- If youth have struggled with previous activities, start them with the Scientist Jaime.
- Emphasize that screens model the distance between the Moon and Earth, so youth must design technologies to gather the information remotely. They may not touch the surface or look behind the screen.
Glossary
Data: information that is collected through scientific investigation
Related Videos
Activity Timing
Taking Shape
Model a remote sensing device called LiDAR by engineering a technology to produce a 3D image of a landscape.
Youth Will Know
- Scientists and engineers use remote sensing devices to gather information about the topographical features of a landscape.
- Engineers often use models to represent the technologies or materials they are investigating.
Activity Downloads
|
A3_Taking_Shape_Educator_Guide
Taking Shape Educator Guide
|
|
|
A3_Taking_Shape_Engineering_Notebook
Taking Shape Engineering Notebook (English)
|
|
|
A3_Taking_Shape_Engineering_Notebook_Spanish
Taking Shape Engineering Notebook (Spanish)
|
Setup
The Educator Guide has a script, materials list, and prep directions. Be sure to have it open and ready to help guide you through every activity.
- Post the Engineering Design Process poster.
- Bundle a handful of straws together using a rubber band or craft foam and tape, to demonstrate how youth can keep the straws packed together in their model LiDAR device.
- Create a Materials Table with the materials listed on Educator Guide p. 41.
Guiding Question
How can we gather information about topography?
Youth Will Do
- Use straws as a model for LIDAR.
- Record information about a surface.
- Discuss limitations of the model.
Did You Know?
- Some animals, such as bats and whales, have evolved the ability to remotely sense their surroundings using sonar, which relies on bouncing sound waves instead of light.
Quick Tips
- Consider playing videos for youth to review LiDAR.
- Encourage youth to try out different materials or combinations to keep the straws together.
- As an alternative to drawing, have groups trace the topography by using the shape of the straw tops held up to paper.
Glossary
LiDAR: (Light Detection And Ranging): a remote sensing technology that collects data from lasers to map the shape of a landscape
Related Videos
Activity Timing
Secret Messages
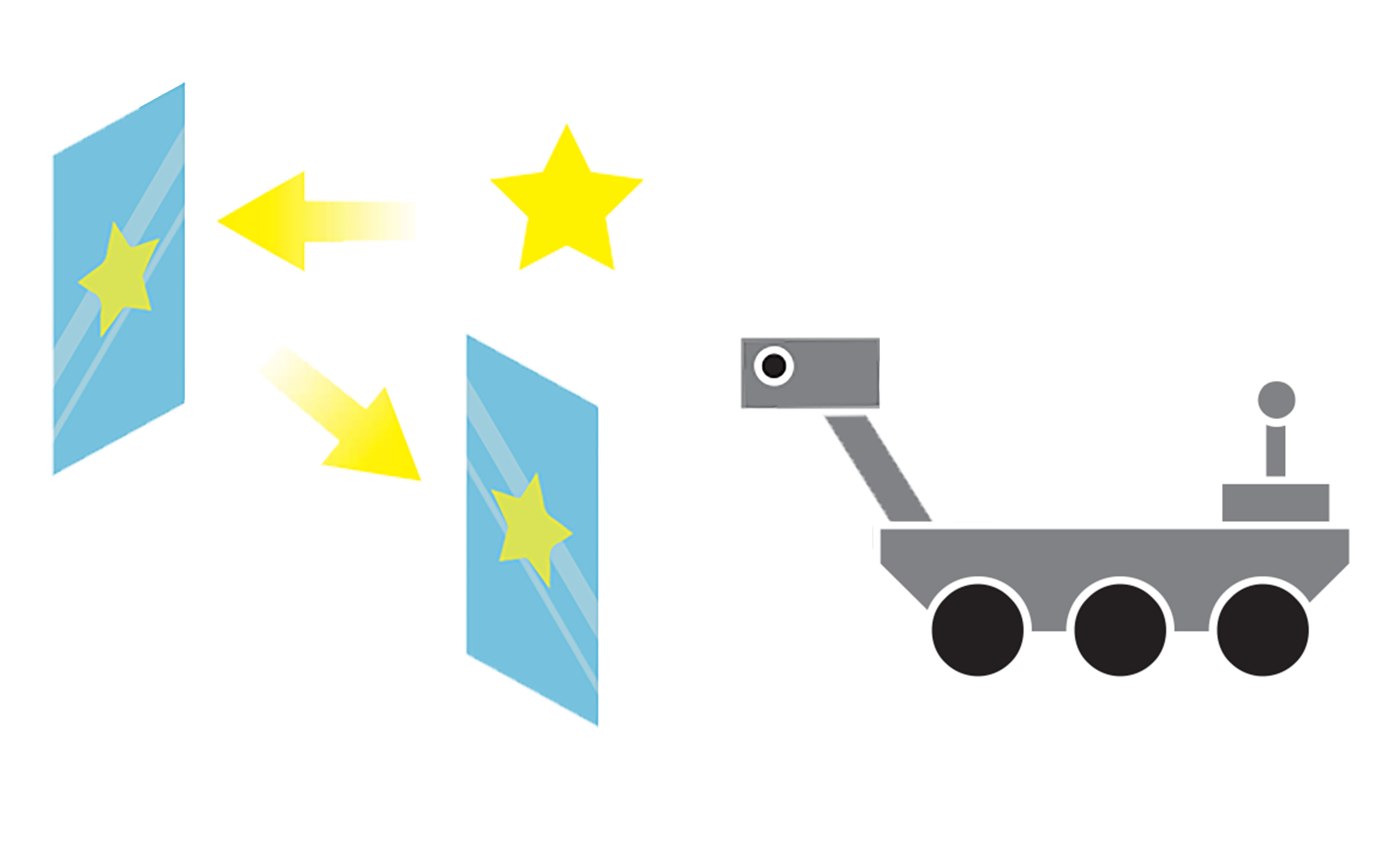
Youth explore how different colored filters work to hide or highlight other colors.
Youth Will Know
- They can combine technologies, like optical filters, with remote sensing devices to reveal information.
- Manipulating colors can help them make sense of complex visual data.
Activity Downloads
|
A2_Secret_Messages_Educator_Guide
Secret Messages Educator Guide
|
|
|
A2_Secret_Messages_Engineering_Notebook
Secret Messages Engineering Notebook (English)
|
|
|
A2_Secret_Messages_Engineering_Notebook_Spanish
Secret Messages Engineering Notebook (Spanish)
|
Setup
The Educator Guide has a script, materials list, and prep directions. Be sure to have it open and ready to help guide you through every activity.
- Post the Engineering Design Process poster.
- Draw the Optical Filter Investigations chart, Educator Guide p. 36, on chart paper and post it near the EDP poster.
- Create a Materials Table with the materials listed on Educator Guide p. 25.
Guiding Question
How can we gather remote sensing data to help scientists find out about minerals from a distance?
Youth Will Do
- Manipulate light and color to reveal visual information.
Did You Know?
- Since Mars is very red, planetary scientists use optical filters to highlight colors they wouldn't see or notice otherwise.
Quick Tips
- It is very difficult to make indiscernible messages. Focus youth on the difference rather than trying to achieve a truly hidden message.
- If groups finish early, have them use extra folders and tape to combine their optical filters with familiar technologies, like glasses.
Glossary
Optical Filter: a technology that manipulates light and color to help reveal visual information